Shaft couplers join two shafts together to transfer power from the driveshaft to the driven shaft while compensating for minor shaft misalignments and mounting mistakes. Mechanisms requiring power transmission, including pumps, motors, generators, compressors, turbines, machines, engines, and shaft couplers, are frequently used. Read More…
Our shaft couplings are the best around! Not only do we provide you with exceptional levels of customer service but we also provide you with manufacturing and a repair service that you can count on. We are also capable of providing you with special designs. That’s right! Our design team will work closely with you in order to ensure that you are getting the product that will fit your specific...
At Coupling Corporation of America, we devote ourselves to engineering shaft couplings that deliver exceptional precision, durability, and performance for complex motion control and power transmission applications. We design each coupling to accommodate the unique torque, misalignment, vibration, and speed demands of our customers’ equipment, ensuring smooth, efficient operation even under...
Ruland’s carefully made shaft collars, rigid shaft couplings & zero backlash motion control flexible shaft couplings, including beam, Oldham & bellows couplings, are available in both inch & full-metric dimensions. Our line has expanded to include metric shaft collars, metric rigid couplings & step bore rigid couplings. For 70 years, we have supplied custom-made products to meet special needs.
Founded in Buffalo, NY in 1946, Power Drives, Inc. (PDI) designs and manufactures custom-engineered hose and tube assemblies for original equipment manufacturers (OEM), and engineered systems for locomotives and other mobile equipment. PDI also distributes a wide range of hydraulic, pneumatic and electromechanical components for fluid conveyance, motion control and power transmission applications ...
More Shaft Coupler Manufacturers
Shaft couplers offer mechanical flexibility to enable smooth rotation of the shafts and lower the risk of equipment failure by reducing wear, impact, vibration, and noise. In situations where the motor and the workpiece are securely fastened and closely coupled, minute misalignments might develop over time due to temperature changes and the passage of time, which can cause vibration and damage. Therefore, shaft couplings are crucial in lowering shock and vibration while enabling smooth rotation.

Uses of Shaft Couplers
The four main uses of shaft couplers are power transmission, joining misaligned shafts, decreasing shocks and friction, and simple assembly and disengagement.
Joining Misaligned Shafts
Even though both shafts have identical specifications, the alignment and shaft positioning precision can still be impacted by machining mistakes. High-precision alignment of the driven and drive shaft placement is challenging and time-consuming.

The power transmission system suffers when shaft misalignments are present. Misalignment results from thermal expansion or loss of alignment and placement by motion-related vibrations, movements, or bumps. As the shafts spin, unwanted forces are applied to the nearby components, resulting in noise and vibration. Due to the stress produced by the misalignment, it also causes more wear and increases the chance of mechanical failure. A shaft coupler must be employed to correct such mounting and placement mistakes.
Decreasing Shocks and Friction
In many cases, shaft couplings shield neighboring parts. As a result, they reduce vibration, which compromises the precision of others. They also lessen the impact of shock loads or torque changes when applied to different shafts. In addition, flexible couplings can offer electrical isolation when driving delicate electronic components in a high-voltage environment.

Shaft couplings stop heat from the power source from transferring to the driving shaft. The precision of the surrounding components degrades due to thermal expansion, which causes the components to move from their proper location.
Power Transmission
Shaft couplers' main use is to transmit power between two shafts. Therefore, when connected by a shaft coupling, the driveshaft transmits power to the driven shaft. A power source rotates the driveshaft, which can either be electrical or mechanical. The powered shaft is subsequently made easier to rotate by the shaft coupling.
Using a one-piece shaft might result in errors and is costly and cumbersome to carry, assemble, and maintain. In addition, a one-piece shaft must be completely replaced if it breaks. Using two-coupled shafts is a more sensible choice as it allows power transfer between two shafts with different diameters.
Types of Shaft Couplers
Depending on the application, there are various types of shaft couplings available in two categories: flexible couplings and rigid shaft couplings.
Chain Couplings
Chain couplings can transmit up to thousands of horsepower and are ideal for power transmission applications. Misalignment allowances are typically 2 degrees and 0.015 inches (0.381 mm) for angular and parallel misalignment, respectively. Standard chain couplings use double big roller chains and unique chain sprockets, whose clearances allow the design to work as a flexible coupling.

Gear Couplings
The flange connection has been modified into a gear coupling. The flange but also its hub are independent components in these connections. The flange's internal gear teeth align with the protruding gear teeth on the hubs' external diameter.

Grid Couplings
Grid couplings are made of two hubs with radial slots and a winding length of spring steel woven between them. The spring steel provides the coupling's torsional flexibility, which can endure a wide variety of torque, speed, and misalignments. The spring steel's contact length with the hub teeth shortens as the load does. Misalignments are accommodated by flexing the spring steel. Grid couplings are good at dampening vibration and absorbing shock. The grid coupling needs to be periodically greased and secured tightly to preserve lubrication and avoid contamination to maintain its functionality and efficiency.

Tire Couplings
Tire couplings connect the two hubs with a substantial polyurethane, rubber, or polyether part. Under shear, the element transmits the torque. Tire couplings may accommodate severe alignment issues while minimizing shock and vibration transmission. They can move at moderate to high speeds while transmitting a wide range of torque.
Other types of couplings include:
- Disc Coupling
- Diaphragm Coupling
- Beam Coupling
- Bellows coupling
- Fluid Coupling
Shaft Coupling Considerations
Shaft Coupling Windup
All shaft couplings contain windups. When one shaft's torque is larger than the other, a phenomenon known as shaft torsional deflection or coupling windup occurs. The motion control systems' placement becomes erroneous due to this loss of motion.
High Power Applications
Flexible shafting is required by everything from 600 MW steam turbines to kitchen food mixers. The diameter, wall thickness, and bending rigidity of the shaft all increase with increasing torque. Any imposed motion creates bending stress, which swiftly results in fatigue failure. Axial and parallel offsets are the most common types of imposed motion. It is particularly crucial to reduce this component.
Choosing the Proper Shaft Coupler Supplier
To make sure you have the most productive outcome when purchasing a shaft coupler from a shaft coupler supplier, it is important to compare at least 4 to 5 companies using our shaft coupler directory. Each shaft coupler supplier has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or request a quote. Review each shaft coupler company website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple shaft coupler companies with the same form.






 Ball Bearings
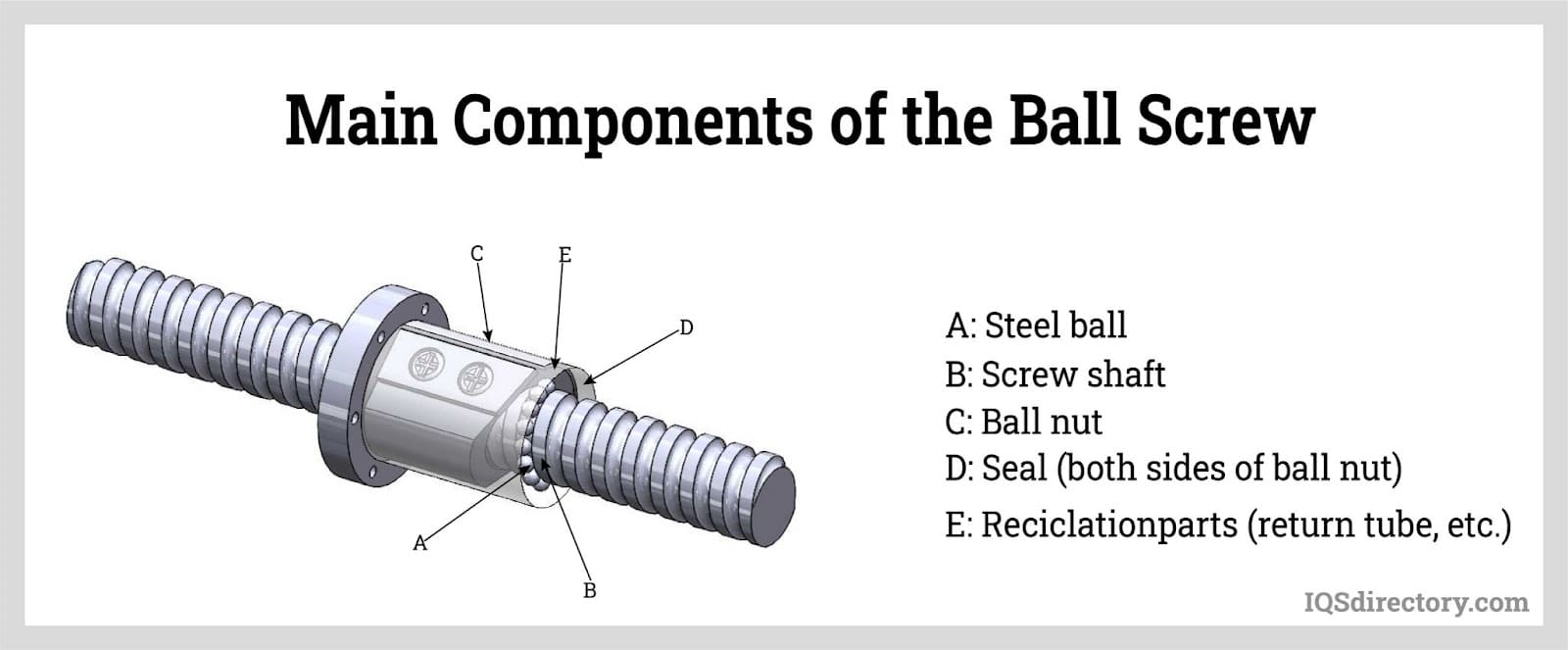
Ball Bearings Ball Screws
Ball Screws Electric Motors
Electric Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials Gears
Gears Quick Release Couplings
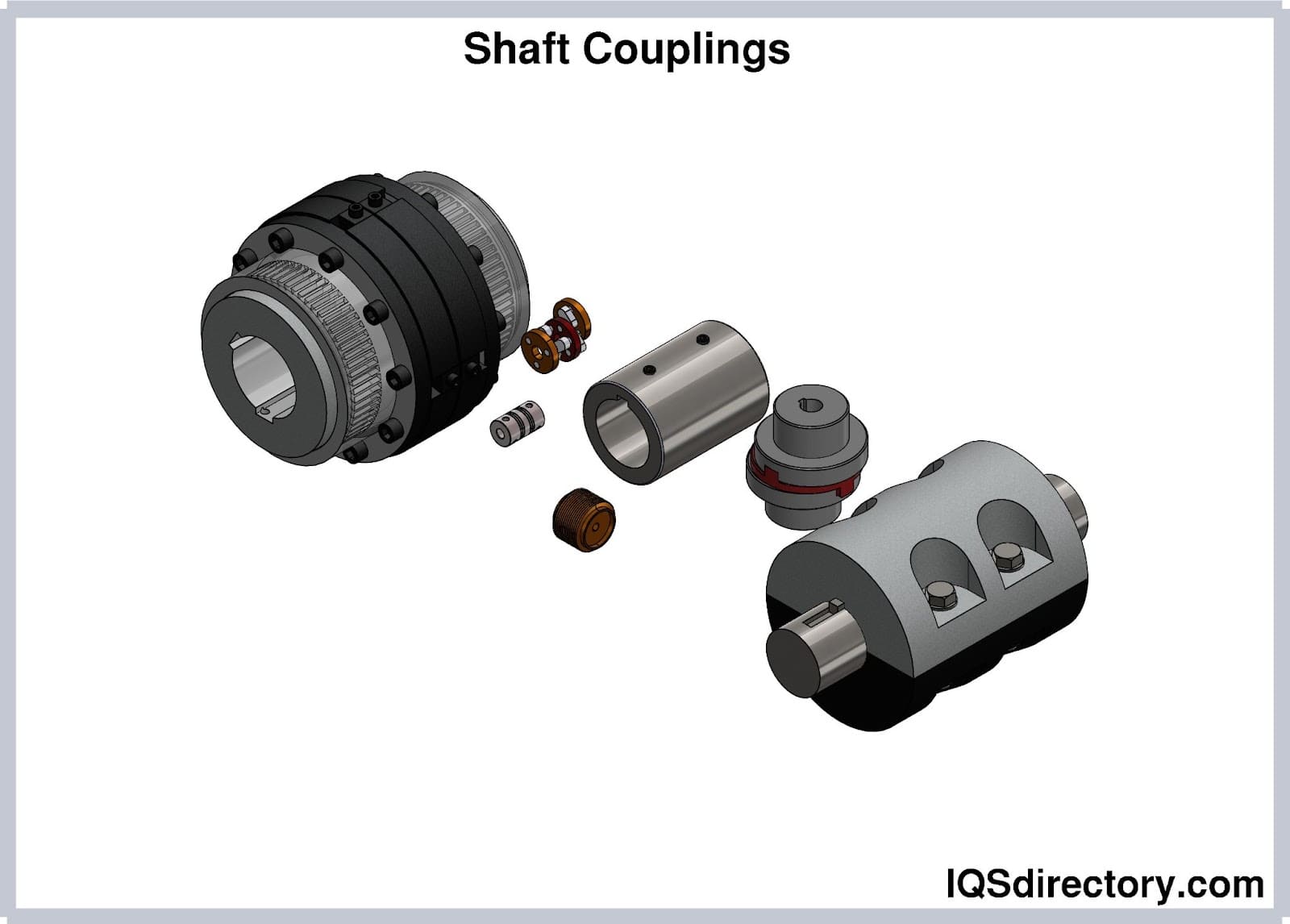
Quick Release Couplings Shaft Couplings
Shaft Couplings Speed Reducers
Speed Reducers Timing Belting
Timing Belting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services